See Explanation
[]
Endocrine
throid disorders
thyrotoxicosis
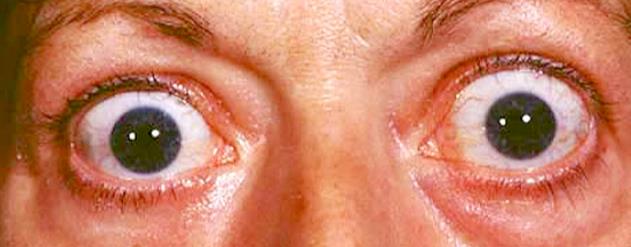
A 42-year-old male presents to the outpatient clinic reporting persistent fatigue, noticeable palpitations, and an unintentional 5 kg weight loss over the past several months. He also describes significant bilateral eye irritation, excessive tearing, and a feeling of grittiness. His past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.3°C, blood pressure is 145/85 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and regular, and respirations are 19/min. Examination of his eyes reveals mild periorbital edema and scleral injection, with noticeable lid lag upon downward gaze but no obvious proptosis. His thyroid gland appears diffusely enlarged on palpation but is non-tender. The remainder of his physical examination is unremarkable. Initial laboratory results obtained a week prior showed a serum calcium level of 2.65 mmol/L (normal 2.18-2.58 mmol/L), with a suppressed parathyroid hormone level of 1.1 pmol/L (normal 1.6-9.3 pmol/L). His alkaline phosphatase was elevated at 215 IU/L (normal 50-136 IU/L). Considering the patient's comprehensive presentation and laboratory findings, including recent thyroid function tests, what is the most appropriate primary initial management strategy for his clinical presentation and the associated hypercalcemia?
| Lab Parameter | Value | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | 132 g/L | 125–170 g/L |
| Mean corpuscular volume | 82 fL | 80–100 fL |
| Creatinine | 75.00 µmol/L | 50–90 µmol/L |
| Calcium | 2.65 mmol/L | 2.18–2.58 mmol/L |
| Parathyroid hormone | 1.1 pmol/L | 1.6–9.3 pmol/L |
| 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D | 60 pmol/L | 64-226 pmol/L |
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D | 70 nmol/L | 75–250 nmol/L |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 215 IU/L | 50–136 IU/L |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 35 IU/L | 15–37 IU/L |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 30 IU/L | 17–63 IU/L |
| Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) | 0.01 mIU/L | 0.4-4.0 mIU/L |
| Free Thyroxine (FT4) | 35 pmol/L | 12-22 pmol/L |
Edit question